The Significance of APIs in Business Process Automation: Shopygo BPA
- Athul Raj
- Mar 14, 2022


Companies can choose from a wide range of innovative process transformation and automation solutions. AI, BPA, and ML are some of the most commonly used acronyms in today's information technology industry. Both RPA and BPA are acronyms for process automation technologies that have the potential to increase workplace productivity and efficiency.
For example, when robotics process automation is used in conjunction with business process automation, it is not used in isolation. Investigate these two ideas further to see if they have the potential to increase your company's profitability. Despite their diverse meanings, these two phrases are frequently used interchangeably.


Here are some simple definitions to help you distinguish between these initialisms. We'll use these definitions to help you understand what you need to know:
RPA, or robotic process automation, is the use of a specific type of software to develop automated, rules-based "robot" programs that perform fundamental manual operations efficiently. RPA removes these jobs from human hands and performs them more quickly, correctly, and without the need for pauses.
Business process automation, or BPA, also employs software tools to automate tasks that would otherwise necessitate manual human intervention. However, the scope of BPA is wider and more sophisticated than that of RPA. Instead of utilizing a software robot to copy and paste text, it can use automation to improve the efficiency of the entire operation.

RPA entails tasks performed at an individual employee's desk rather than the sum of all work performed by employees collectively. Consider a knowledge worker in a back office who is in charge of maintaining dozens of Microsoft Excel spreadsheets with data copied from web portals or enterprise software. These tasks take a long time, have a significant risk of introducing unintentional errors, and divert an employee's attention to relatively unskilled duties.
RPA software monitors and learns the sequence of events that human employees follow, then replicate them at a far faster rate and with almost no chance of error. This is only one example of how RPA may be used; numerous jobs can be streamlined using these tools.
RPA is great for on-the-ground automation, but it has limitations. At this point, BPA enters the scene.

The basic objective of BPA and the technologies that enable its implementation is to make entire processes more efficient from start to finish.
Workflows frequently have processes that span numerous business departments. Manual human intervention is required at these stages for a variety of reasons. A completed procedure in one department may require a handoff to another team, or data may need to travel between various computer systems. While RPA can integrate automation at the individual step level, BPA can alleviate "invisible" slowdowns by connecting these independently automated stages.

Workflows become more efficient when firm tasks are automated (BPA). Rather than focusing on a single department, BPA is creating software solutions that combine all of its existing processes. BPA takes a comprehensive strategy to prevent becoming entangled in a single stage of the process.
When it comes to business process automation, however, a thorough evaluation of the organization's inefficiencies is usually required to find the most serious difficulties. As a result, these activities are founded on the pillars of corporate operations, which range from quick account setup to real-time delivery of promotional deals to prospective clients.
Business procedures make it possible for several departments to collaborate more successfully and profitably. For example, BPA is used as the foundation for both an enterprise resource planning (ERP) and a customer relationship management (CRM) system. These company automation benefits can be obtained while spending less money, increasing employee productivity, and creating satisfied customers.
BPA's main takeaways:

A survey says that 95% of corporate respondents desire to adopt RPA to boost efficiency. RPA software allows for the development, deployment, and management of self-driving software robots that mimic human behavior and interact with digital systems and software. Software robots, like humans, may perform a variety of tasks by interpreting what they see on the screen and selecting the relevant buttons. Software robots are faster and more trustworthy than people because they do not need to get up and stretch or grab a cup of coffee.
Furthermore, robotic process automation improves efficiency, responsiveness, and productivity. Additionally, removing time-consuming chores from the workday has a variety of benefits, including higher productivity and a more balanced work-life balance for employees.
RPA is also non-intrusive and, when used quickly, can expedite the speed of digital transformation. Another advantage of this technology is that it can automate tasks on systems that lack APIs, virtual desktop interfaces, or data access.


Data entry and file transmission are two tasks that software robots potentially take over for humans. These people can fill out forms, do routine analyses, and provide reports. Using powerful machine learning models, robots can be taught cognitive skills such as reading language, communicating, and processing unstructured data.
Humans may focus on their key talents, such as invention, cooperation, production, and customer service, by automating repetitive, high-volume operations. Businesses benefit from increased productivity, efficiency, and agility. In terms of the future of labor, RPA is a foregone conclusion.
RPA bots run on desktop computers can exploit the current user interface to do human-like tasks like copying and pasting, moving files, and sending emails. The bot records and executes the entire operation without human intervention. Despite the fact that there are a few examples of intelligent bots, the great majority of bots have not yet achieved this degree of intelligence. Screen scraping is a technique used by bots to collect data from internet forms.
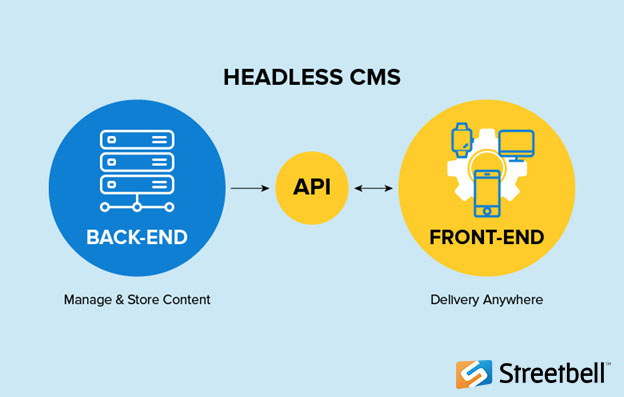
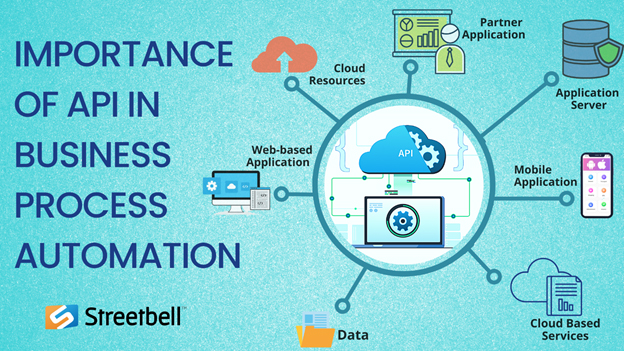
BPA, on the other hand, makes it more difficult to create workflows that integrate a wide range of systems using a uniform processing paradigm. To share and retrieve data, these systems require APIs and database access. To complete this task fast and efficiently, coding and development assistance are required. RPA allows computers to record, learn, and do activities on their own. RPA does not require the use of an API.
As a result, BPA integration takes a more comprehensive approach to the problem. It is advantageous to simplify a company's decision-making process. The basic goal of RPA is to automate time-consuming human tasks. RPA has little impact on day-to-day business operations because it is compatible with pre-existing BPA software such as ERP and CRM.


Yes, RPA can be a supplementary work that helps a business deploy BPA solutions and generate improvements informed by BPM strategy. In fact, RPA has fast become such an integral element of BPM that it can be impossible to distinguish between the two while looking for solutions.
Automating low-level operations is the first step in laying the groundwork for teams working on BPM solutions. However, RPA does not fix intrinsic process inefficiencies; in fact, it may highlight those inefficiencies more clearly. That fact is advantageous to your company because RPA provides information on where you should focus your improvement efforts.


RPA is a subset of BPA that allows for the optimization of important business processes (BPA). When paired with RPA, this strategy delivers significant financial benefits while preserving RPA's efficacy and safety. Rather than RPA, BPA focuses on the strategic and tactical benefits of automation.
Invoices are authorized using software solutions like RPA, and vendor compliance and performance are assessed.
Chat windows on websites are one application of RPA in CRM. If you choose, I can automate your chat windows. These bots deliver the data they collect to a human employee, who engages with the customer directly. Bots are commonly used in procurement automation to undertake operations that were previously performed by humans, such as form filling, email analysis, and the creation of vendor-specific forms.
Furthermore, BPA is a little intrusive in terms of integration. It is feasible to build a new system by replacing it with a self-contained system that runs its own software. Each BPA division is linked by a single system, which streamlines and automates the entire process. The BPA is in charge of making sure everything runs smoothly.
To recap, RPA focuses on tasks, but BPA focuses on revamping the way you work through a bigger strategy influenced by best practices in business process management. Taking use of the benefits of these concepts and techniques can result in increased productivity and a lower bottom line. Your company does not need to stage a battle between RPA and BPM because these technologies are not incompatible—they simply require different applications.